[MPC] Linear Parameter-Varying - Model Predictive Control for Racing
Planning and control for autonomous racing vehicles. This project allows you to solve the autonomous racing driving problem using advanced control theory. Particularly, here it is presented a collaborative work using optimal strategies. The Model Predictive Control (MPC) strategy is used online for computing the optimal trajectory maximizing vehicle velocity but also for computing the optimal control actions that make the vehicle to follow the computed references. All the algorithms are solved in real time employing the Operator Splitting Quadratic Program (OSQP) solver.
The vehicle model
The planning-control-estimation diagram shows the interconnection between:

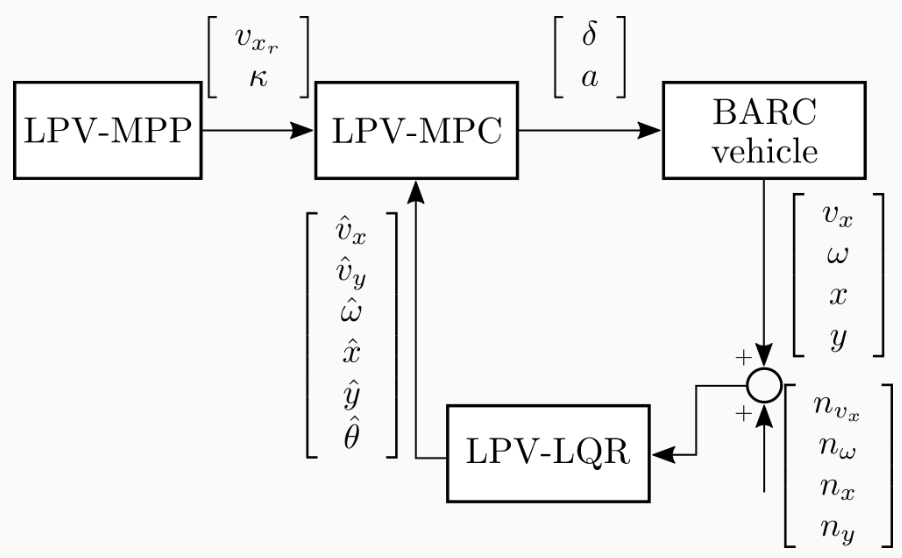
- Planning Module: Generates optimal trajectory using LPV-MPC
- Control Module: Tracks the planned trajectory
- Estimation Module: Provides state feedback
LPV modeling
The LPV (Linear Parameter-Varying) paradigm allows to represent a given non-linear representation into a pseudo-linear form:
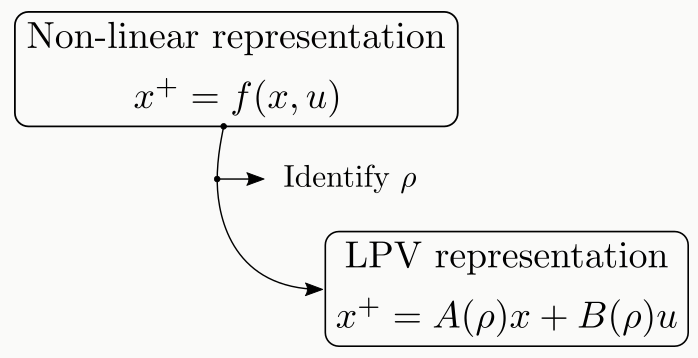
This approach enables real-time optimization while maintaining the nonlinear vehicle dynamics characteristics.
The vehicle model
The model used in planning, control and estimation algorithms is the bicycle representation where the inputs are:
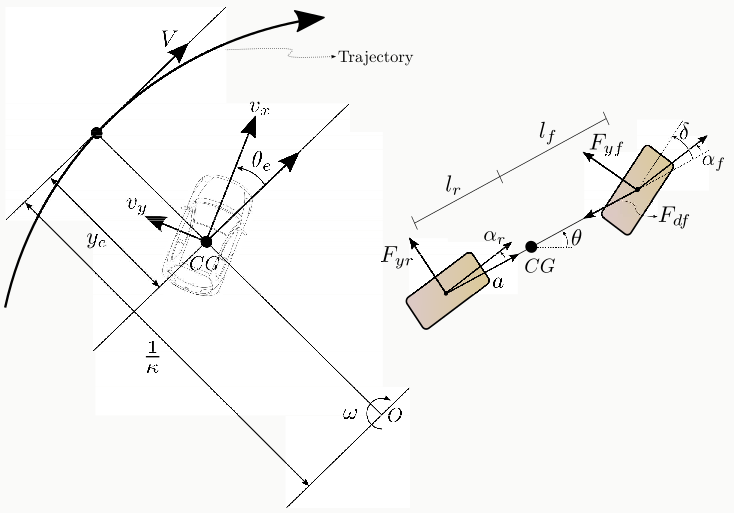
- Front steering angle (δ): Controls the lateral motion
- Rear wheel linear acceleration (a): Controls the longitudinal motion
The bicycle model captures the essential vehicle dynamics while remaining computationally efficient for real-time MPC implementation.
MPC for planning
The trajectory planning for racing is solved using the MPC technique. The cost function addresses the lap time minimization as well as the smoothness of the lateral motion by reducing as much as possible the understeer and oversteer behaviours. This algorithm is launched every 33 ms.
MPC for control
At this point an MPC is built and solved at every control iteration (33 ms) to figure out the optimal control actions (steering and rear wheel acceleration).
Test
To use this project, install it locally via:
git clone https://github.com/phatcvo/LPV-MPP-MPC-for-racing.gitTo execute the code, run:
catkin_make (to create build and devel folders)
source devel/setup.bash
roslaunch barc MAIN_LAUNCH.launch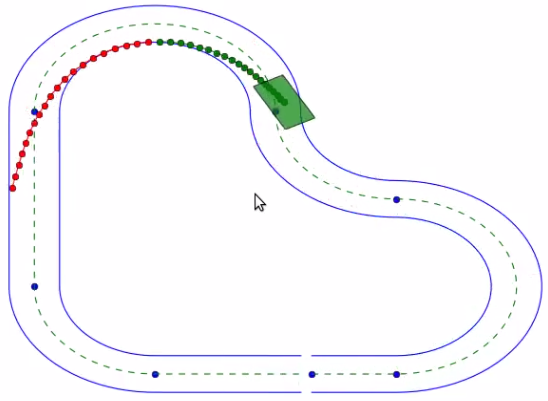
Note: This project demonstrates the LPV-MPC approach for autonomous racing vehicles with real-time trajectory planning and control.
References
Trajectory planner presented in: Alcala, E., Puig, V. & Quevedo, J. (2019). LPV-MP Planning for Autonomous Racing Vehicles considering Obstacles. Robotics and Autonomous Systems.
Controller presented in: Alcala, E., Puig, V., Quevedo, J., & Rosolia, U. (2019). Autonomous Racing using Linear Parameter Varying - Model Predictive Control (LPV-MPC). Control engineering practice.
Estimator presented in: Alcala, E., Puig, V., Quevedo, J., & Escobet, T. (2018). Gain-scheduling LPV control for autonomous vehicles including friction force estimation and compensation mechanism. IET Control Theory & Applications, 12(12), 1683-1693. (https://digital-library.theiet.org/content/journals/10.1049/iet-cta.2017.1154).